Tokenisation of financial securities
Table of contents
1-Tokenised securities on distributed ledger technology (DLT)
2-A technology applied in the financial markets
3-Tokenisation of assets for the issuer and the funder
A revolution in the financial markets:
Developments in financial services are shaping society as we know it today. In particular, the creation of the joint stock company and the stock market has had lasting geopolitical effects on a global scale. The consequences of these innovations, and with-in them the democratisation of capital markets, are still evident today. Now we are witnessing transformations that are revolutionising the stock market: the tokenisation of corporate assets. This new concept has become a source of considerable value on a global scale and will help to make markets more efficient and fairer…
1- Tokenised securities on distributed ledger technology (DLT)
The arrival of tokenised assets marks the beginning of a process similar to the creation of joint stock companies and the opening of the first stock exchange in 1602. Thus, financial products found their way onto a Universal Trading Platform (UTP) where all stock exchange products are traded and negotiated on European markets.
The tokenisation of an asset is the conversion of the rights attached to the asset into a digital token (Security Tokens). While the process itself is similar to asset securitisation, tokenisation uses distributed ledger technology (DLT) and the Blockchain.
Blockchain technology offers many major advantages over conventional technologies used by financial services companies.
First, DLT offer :
– High transparency to all parties, who all have access to the same documents and can only be changed through a clearly defined and secure consensus algorithm.
– It promotes the traceability of each transaction. Transactions are recorded and stored simultaneously on a large number of blockchains, allowing all transactions to be “notarised”.
– The “splitting” of tokenised securities. To allow access to ‘small’ investors with limited means a company can split its securities:
- greatly democratise business finance by making it more accessible;
- increase the depth of liquidity by increasing the number of investors.
- enhanced security because DLT is more secure than traditional manual record keeping. Transactions must be validated before they are recorded and cannot be altered afterwards. – Increased efficiency and speed, as DLT eliminates paper processes and thus the risk of human error. Thus it streamlines processes and reduces the number of intermediaries and thus costs.
2 – Technology applied in the OTC secondary market
Although the advantages of DLT may seem abstract at first glance, they make sense in terms of financing solutions for non-listed companies. Indeed, the use of a tokenised asset, in the financial sector, offers many advantages, starting with the strong disintermediation (reduction of the number of intermediaries), no need to go through a bank, a broker or an exchange. The buyer and seller can interact directly with each other in a synchronised P2P manner to shorten the settlement time of assets. Any funding opportunity is exposed to the global market, by anyone with access to the Internet, wherever they are. Financing and investment projects will benefit from a larger investor community, and will no longer be restricted to professional investors. DLT can significantly reduce market manipulation, as each transaction is recorded in real time and is transparent, shared, unalterable, auditable and accessible to all stakeholders, including regulators, at any time.
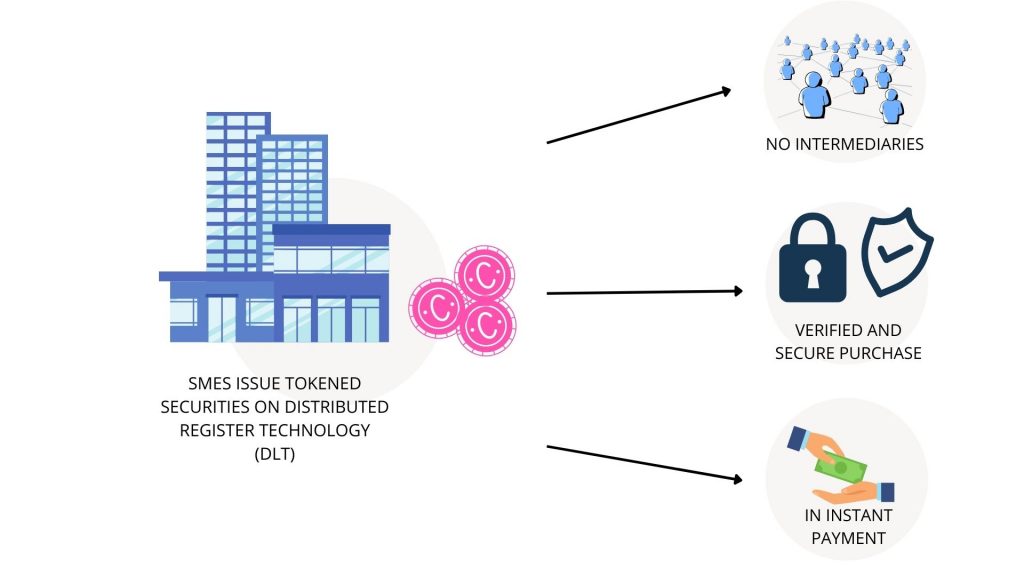
Table of contents
- For the issuers
- For the funders
Tokenisation of assets for the issuer and the funder
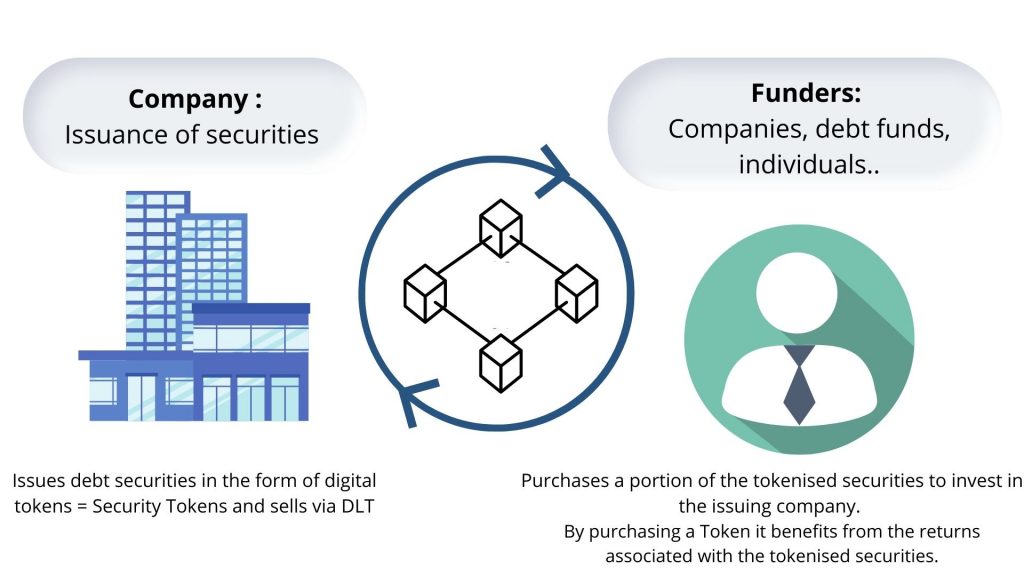
The tokenisation of financial assets is of interest to both the issuer of the token and the investor.
1- Regarding the issuer
Any company can decide to tokenise its assets, thanks to the blockchain. To do so, the company will have to tokenise the identified financial instrument, i.e. the process of attaching a financial instrument and the rights attached to it to a digital token in order to register it on a blockchain.
It will be necessary to determine the rights attached to each token (dividend rights, voting rights, information rights).
The programming of a smart contract is attached to the token in order to encode it electronically (in the form of metadata):
- the conditions of transfer of tokens;
- the transfer of the rights attached to the tokens;
- the payment of dividends.
2 – Regarding the funders
When an investor decides to invest in traditional financial assets, he or she will have several options, including
- The purchase of bonds;
- The purchase of debt securities;
- ….
But these financial securities (claims, bonds, equity securities,…) are not always easily liquidated. By providing a common language and a secondary market, existing assets in the form of tokens can be exchanged more easily.
Thanks to the emergence of decentralised finance, investors in security tokens will eventually be able to value tokens in the DeFi ecosystem. Just like SG forge’s current experiment with MakerDAO.
By valuing this debt for use as collateral, the company can borrow and thus benefit from leverage. This allows the lender to obtain cash, but it will have to pay interest on that cash.
